The Embedded Widget Revolution: Collecting Feedback Without Leaving Your App
Technical guide to embedding lightweight feedback widgets that capture context automatically. Reduce friction to zero and increase feedback quality by 3x.
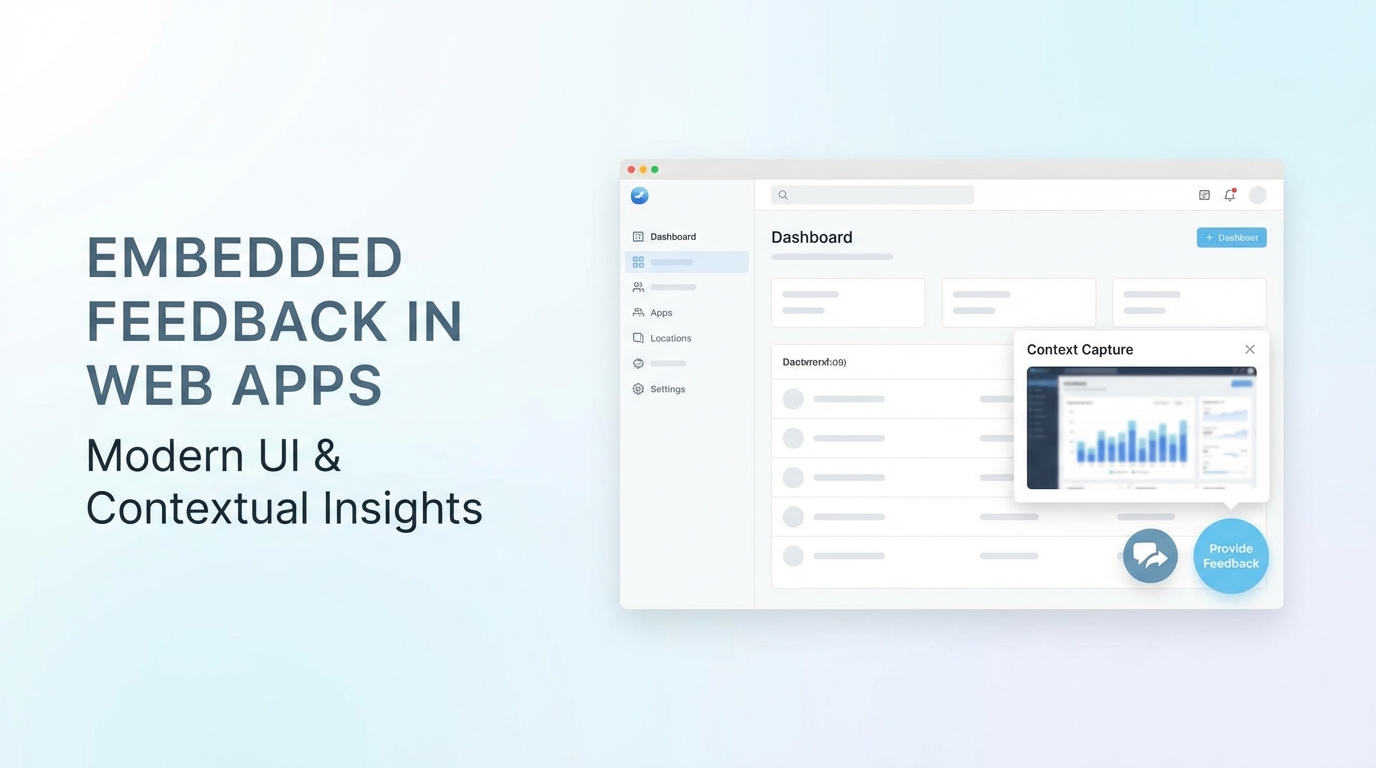
Summary
External feedback tools break user flow and lose context. Embedded widgets collect feedback where users work, automatically capturing page context, user state, and session data. This guide covers the technical implementation of lightweight feedback widgets, context auto-capture strategies, and best practices for frictionless in-app feedback collection.
Why Embedded Beats External
Feedback tools that require users to leave your application face fundamental problems.
The Context Problem
When users click to an external feedback form:
- They lose context of what triggered the feedback
- You lose information about where they were
- Details get forgotten in the transition
- Friction increases abandonment
An embedded widget captures feedback in the moment, with full context automatically attached.
The Friction Problem
Every step between "I have feedback" and "feedback submitted" loses users:
| Feedback Path | Steps | Typical Completion |
|---|---|---|
| External link → new tab → form | 4-5 | 15-25% |
| In-app modal → form | 2-3 | 40-50% |
| Embedded widget → conversation | 1-2 | 60-70% |
Embedded widgets minimize steps and maximize completion.
The Context Capture Advantage
Embedded widgets know things external forms can't:
- Current page/route
- User identity and account
- Session duration and history
- Feature being used
- Recent actions taken
- Error states encountered
This context transforms vague feedback into actionable intelligence.
Widget Architecture
A well-designed feedback widget balances functionality with performance.
Core Components
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Host Application │
│ │
│ ┌─────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ Widget Container │ │
│ │ ┌─────────────────────────────┐ │ │
│ │ │ Trigger (Button/FAB) │ │ │
│ │ └─────────────────────────────┘ │ │
│ │ ┌─────────────────────────────┐ │ │
│ │ │ Feedback Interface │ │ │
│ │ │ - Form / Conversation │ │ │
│ │ │ - Screenshot capture │ │ │
│ │ │ - Context display │ │ │
│ │ └─────────────────────────────┘ │ │
│ └─────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────┘
Trigger: Visible entry point (floating button, menu item, keyboard shortcut) Container: Isolated widget wrapper (shadow DOM or iframe) Interface: The feedback collection UI itself Context layer: Auto-capture and enrichment
Loading Strategy
Widgets should never impact application performance.
Async loading:
<script async src="https://widget.uservibes.ai/v1/widget.js"></script>
Deferred initialization:
// Widget loads but doesn't execute until needed
window.UserVibes = window.UserVibes || [];
window.UserVibes.push(['init', { projectId: 'your-project-id' }]);
Lazy component loading:
// Full widget UI loads only when triggered
const openWidget = async () => {
const { FeedbackWidget } = await import('@uservibes/widget');
FeedbackWidget.open();
};
Isolation Patterns
Widgets must not interfere with host application styles or behavior.
Shadow DOM approach:
class FeedbackWidget extends HTMLElement {
constructor() {
super();
const shadow = this.attachShadow({ mode: 'closed' });
shadow.innerHTML = `
<style>/* Widget styles isolated here */</style>
<div class="widget-container">...</div>
`;
}
}
customElements.define('feedback-widget', FeedbackWidget);
Iframe approach:
const iframe = document.createElement('iframe');
iframe.src = 'https://widget.uservibes.ai/frame';
iframe.style.cssText = 'border:none;position:fixed;bottom:20px;right:20px;';
document.body.appendChild(iframe);
Each approach trades off isolation vs. context access:
| Approach | Style Isolation | Event Isolation | Context Access |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shadow DOM | High | Medium | Full |
| Iframe | Complete | Complete | Via postMessage |
| CSS scoping | Medium | None | Full |
Auto-Capture Implementation
The magic of embedded widgets is automatic context capture.
Page Context
Capture where feedback originated:
const capturePageContext = () => ({
url: window.location.href,
path: window.location.pathname,
title: document.title,
referrer: document.referrer,
timestamp: new Date().toISOString(),
});
User Context
Capture who is providing feedback:
const captureUserContext = () => ({
// From your auth system
userId: window.currentUser?.id,
email: window.currentUser?.email,
plan: window.currentUser?.subscription?.plan,
accountAge: daysSince(window.currentUser?.createdAt),
// From session
sessionId: getSessionId(),
sessionDuration: getSessionDuration(),
});
Environment Context
Capture technical environment:
const captureEnvironment = () => ({
userAgent: navigator.userAgent,
language: navigator.language,
screenSize: `${window.screen.width}x${window.screen.height}`,
viewport: `${window.innerWidth}x${window.innerHeight}`,
colorScheme: window.matchMedia('(prefers-color-scheme: dark)').matches ? 'dark' : 'light',
timezone: Intl.DateTimeFormat().resolvedOptions().timeZone,
});
Action History
Capture recent user actions:
// Track significant actions
const actionHistory = [];
const MAX_HISTORY = 20;
export const trackAction = (action, details = {}) => {
actionHistory.push({
action,
details,
timestamp: Date.now(),
path: window.location.pathname,
});
if (actionHistory.length > MAX_HISTORY) {
actionHistory.shift();
}
};
// Usage in your app
trackAction('button_click', { button: 'export' });
trackAction('page_view', { page: 'dashboard' });
trackAction('error', { message: 'Failed to load data' });
Error Capture
Automatically capture JavaScript errors:
const errorHistory = [];
window.addEventListener('error', (event) => {
errorHistory.push({
message: event.message,
source: event.filename,
line: event.lineno,
column: event.colno,
timestamp: Date.now(),
});
});
window.addEventListener('unhandledrejection', (event) => {
errorHistory.push({
type: 'unhandled_promise',
reason: event.reason?.message || String(event.reason),
timestamp: Date.now(),
});
});
Screenshot Capture
Allow users to annotate screenshots:
import html2canvas from 'html2canvas';
const captureScreenshot = async () => {
const canvas = await html2canvas(document.body, {
ignoreElements: (el) => el.classList.contains('feedback-widget'),
logging: false,
});
return canvas.toDataURL('image/png');
};
Privacy consideration: Always let users review and redact screenshots before submission.
Widget Interface Patterns
The feedback interface itself impacts completion rates.
Conversation vs. Form
Form pattern:
┌────────────────────────────┐
│ What's your feedback? │
│ ┌────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ [Text area] │ │
│ │ │ │
│ └────────────────────────┘ │
│ Category: [Dropdown ▼] │
│ [ ] Include screenshot │
│ [Submit] │
└────────────────────────────┘
Conversation pattern:
┌────────────────────────────┐
│ 🤖 What's on your mind? │
│ │
│ The export is broken │
│ You │
│ │
│ 🤖 I'm sorry to hear that. │
│ Which export are you │
│ trying to use? │
│ │
│ ┌────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ Type your message... │ │
│ └────────────────────────┘ │
└────────────────────────────┘
Conversation patterns yield richer feedback but require more sophistication to implement.
Progressive Disclosure
Start minimal, expand as needed:
Initial state: Simple text input + submit After typing: Category selector appears If bug-related: Screenshot option appears If detailed: Structured fields expand
Quick Actions
For common feedback types, provide shortcuts:
┌────────────────────────────┐
│ What would you like to do? │
│ │
│ 🐛 Report a bug │
│ 💡 Suggest a feature │
│ ❓ Ask a question │
│ 💬 Other feedback │
└────────────────────────────┘
Each option can branch to a tailored flow.
Integration Patterns
Widgets need to communicate with your backend and fit your tech stack.
React Integration
import { FeedbackWidget } from '@uservibes/react';
function App() {
const user = useCurrentUser();
return (
<>
<YourApp />
<FeedbackWidget
projectId="your-project-id"
user={{
id: user.id,
email: user.email,
name: user.name,
}}
metadata={{
plan: user.plan,
accountId: user.accountId,
}}
/>
</>
);
}
Vue Integration
<template>
<div>
<YourApp />
<FeedbackWidget
:project-id="projectId"
:user="currentUser"
:metadata="metadata"
/>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { FeedbackWidget } from '@uservibes/vue';
import { useAuth } from './composables/auth';
const { currentUser } = useAuth();
const projectId = 'your-project-id';
const metadata = computed(() => ({
plan: currentUser.value?.plan,
}));
</script>
Vanilla JavaScript
// Initialize
UserVibes.init({
projectId: 'your-project-id',
position: 'bottom-right',
});
// Set user context (call after login)
UserVibes.identify({
userId: user.id,
email: user.email,
traits: {
plan: user.plan,
company: user.company,
},
});
// Programmatic triggers
document.getElementById('feedback-btn').onclick = () => {
UserVibes.open({ type: 'feature-request' });
};
Event Hooks
Subscribe to widget events for custom handling:
UserVibes.on('open', () => {
analytics.track('Feedback Widget Opened');
});
UserVibes.on('submit', (feedback) => {
analytics.track('Feedback Submitted', {
type: feedback.type,
hasScreenshot: !!feedback.screenshot,
});
});
UserVibes.on('close', () => {
// Clean up if needed
});
Performance Best Practices
Widgets must be invisible to performance metrics.
Bundle Size
Keep widget payload minimal:
| Component | Target Size | Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Core loader | < 5KB | Inline critical, defer rest |
| Full widget | < 50KB | Code split, lazy load |
| With screenshots | < 100KB | Load html2canvas on demand |
Load Timing
Don't block critical path:
// Load after page is interactive
if (document.readyState === 'complete') {
loadWidget();
} else {
window.addEventListener('load', loadWidget);
}
Network Strategy
Minimize requests:
// Batch context updates
const contextBuffer = [];
const flushContext = debounce(() => {
if (contextBuffer.length) {
api.updateContext(contextBuffer);
contextBuffer.length = 0;
}
}, 1000);
Memory Management
Clean up properly:
class FeedbackWidget {
destroy() {
// Remove event listeners
this.listeners.forEach(({ target, event, handler }) => {
target.removeEventListener(event, handler);
});
// Clear intervals
this.intervals.forEach(clearInterval);
// Remove DOM elements
this.container.remove();
}
}
Key Takeaways
-
Embedded beats external: In-app widgets capture context and reduce friction that external tools can't match.
-
Auto-capture is essential: Page, user, environment, actions, and errors should be captured automatically—not asked for.
-
Isolation protects both sides: Shadow DOM or iframes ensure widget styles don't leak and host styles don't break the widget.
-
Performance must be invisible: Async loading, lazy initialization, and minimal bundle size ensure widgets don't impact your application.
-
Conversation captures more: Guided dialogue extracts richer, more actionable feedback than form fields.
-
Progressive disclosure reduces friction: Start simple, expand based on feedback type and user engagement.
-
Integrate with your stack: SDKs for React, Vue, and vanilla JS make embedding straightforward while maintaining type safety.
User Vibes OS provides embeddable feedback widgets with AI-powered conversations and automatic context capture. See the widget in action or read the integration docs.
Related Articles
Feedback for Developer Tools: Unique Challenges of Collecting from Technical Users
Developers hate surveys but love fixing problems. Learn how to collect actionable feedback from technical users through GitHub issues, API logs, and community channels.
Feedback During Incidents: Turning Downtime and Outages into Improvement Opportunities
How to collect and use feedback during service disruptions. Balance communication, gather impact data, and emerge with stronger customer relationships and clearer priorities.
Feature Flags Meet Feedback: Validating Releases with Real User Signals
Learn how to pair feature flag rollouts with targeted feedback collection to measure impact and catch regressions before full deployment.
Written by User Vibes OS Team
Published on January 10, 2026